accumulated earnings tax c corporation
The accumulated earnings tax is considered a penalty tax to those C corporations that have accumulated over 250000 in earnings 150000 for PSC corporations and if that excess amount has not been distributed to shareholders in the form of a dividend. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act reduced the corporate tax rate from 35 percent to 21 percent providing Read More.
The accumulated earnings tax imposed by section 531 shall apply to every corporation other than those described in subsection b formed or availed of for the purpose of avoiding the income tax with respect to its shareholders or the shareholders of any other corporation by permitting earnings and profits to accumulate instead of being divided or distributed.

. When the revenues or profits are above this level the firm will be subjected to accumulated earnings tax if they do not distribute the dividends to shareholders. For C corporations the current accumulated retained earnings threshold that triggers this tax is 250000. Breaking Down Accumulated Earnings Tax.
If that tax is owed for. Our system imposes a 20 percent tax on accumulated taxable income of a corporation availed of to avoid tax to shareholders by permitting earnings and profits to accumulate rather than being paid out. Imposition of the accumulated earnings tax Section 531 imposes a 20 AET on a corporations accumulated taxable income.
The computation of accumulated taxable income is generally taxable income less federal taxes charitable deductions without regard to limitations capital losses dividends paid and an accumulated earnings credit4the code provides for a minimum accumulated earnings credit of 250000 per year but an expanded credit is available to the extent. Typical C corporations where shareholders are taxed separately from the company may retain up to 250000 of their earnings before incurring accumulated earnings tax. In this article Cory Stigile provides background on the accumulated earnings tax and explains the steps corporate taxpayers may be able to take if the government begins to more actively audit and litigate the accumulation of profits.
The tax is in addition to the regular corporate income tax and is assessed by the IRS typically during an IRS audit. Accumulated Earnings Tax If a corporation pursues an earnings accumulation strategy where the accumulation is to avoid the tax on dividends rather than having a business purpose then IRC 532 provides an accumulated earnings tax that can be assessed on accumulated earnings with no clear business purpose. The adjustments include a deduction for federal income taxes paid.
As a practical matter the tax is col-. Accumulated EP was taxed at the C corporation level and will be taxed again as a dividend to recipient S corporation shareholders when distributed. A corporation determines this amount by adjusting its taxable income for economic items to better reflect how much cash it has available to make dividend distributions.
The threshold is 25000 without accumulated earning tax. Its inescapable as earnings is taxed at the firm level and also once again as investor rewards. This is because corporations that do not spend retained earnings are.
According to the IRS anything. EP generated in a C corporation are subject to two levels of taxation corporate and shareholder and retain this character even if subsequently owned by an S corporation. S corporations that were formerly C corporations are subject to a special tax if their passive investment income such as dividends interest rents royalties and stock sale gains exceeds 25 of their gross receipts and the S corporation has accumulated earnings and profits carried over from its C corporation years.
An accumulated earnings tax is a tax imposed by the federal government on companies with retained earnings deemed to be unreasonable and in excess of what is considered ordinary. However if a corporation allows earnings to accumulate beyond the reasonable needs of the business it may be subject to. The AEP account is used to determine.
If that tax is owed for. There is a certain level in which the number of earnings of C corporations can get. He accumulated earnings tax AET is imposed by Internal Revenue Code IRC section 531 on C corporations formed or availed of for the purpose of avoiding the imposi-tion of income tax on their shareholders by permitting earnings and profits to be accumulated instead of being distrib-uted.
S corporations that were formerly C corporations are subject to a special tax if their passive investment income such as dividends interest rents royalties and stock sale gains exceeds 25 of their gross receipts and the S corporation has accumulated earnings and profits carried over from its C corporation years. Charitable contributions and any net. Accumulated earnings penalty is accumulated taxable income.
The accumulated earnings tax is a 20 tax that will be applied to C corporations taxable income. The AET is imposed in addition to the regular 21 corporate income tax and falls on the accumulated taxable income of the year or years for which the forbidden purpose is found. C corporations keep an accounting of their undistributed after-tax earnings in profits in a tax record account called accumulated earnings and profits AEP.
The AET is a penalty tax imposed on corporations for unreasonably accumulating earnings. The tax rate on accumulated earnings is 20 the maximum rate at which they would be taxed if distributed. Private and publicly held corporations are subject to this tax but it does not impact passive foreign investment companies tax-exempt organizations and personal holding companies.
S corporations that were formerly C corporations are subject to a special tax if their passive investment income such as dividends interest rents royalties and stock sale gains exceeds 25 of their gross receipts and the S corporation has accumulated earnings and profits carried over from its C corporation years. C Corp Accumulated Earnings And Profits Tax Disadvantages of a C Corporation Having limitless development features a few minor obstacles. There are a lot of fees that come with submitting the Articles of Consolidation.
A corporation can accumulate its earnings for a possible expansion or other bona fide business reasons.

Oh How The Tables May Turn C To S Conversion Considerations Stout
S Corp Rias Disadvantaged By The Tax Bill Mercer Capital

Darkside Of C Corporation Manay Cpa Tax And Accounting

What Is A C Corporation What You Need To Know About C Corps Gusto

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study

How To Calculate The Accumulated Earnings Tax For Corporations Universal Cpa Review

Oh How The Tables May Turn C To S Conversion Considerations Stout

Cares Act Implications On Corporate Earnings And Profits E P

Strategies For Avoiding The Accumulated Earnings Tax Krd

Demystifying Irc Section 965 Math The Cpa Journal
/BOA-f8957c5ee9c14788b59a7e5edd802a7b.jpg)
Which Transactions Affect Retained Earnings

Understanding The Accumulated Earnings Tax Before Switching To A C Corporation In 2019
Solved Please Note That This Is Based On Philippine Tax System Please Put Course Hero

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study

Earnings And Profits Computation Case Study
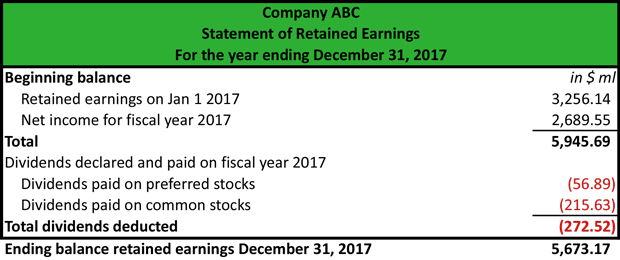
What Are Accumulated Earnings Definition Meaning Example
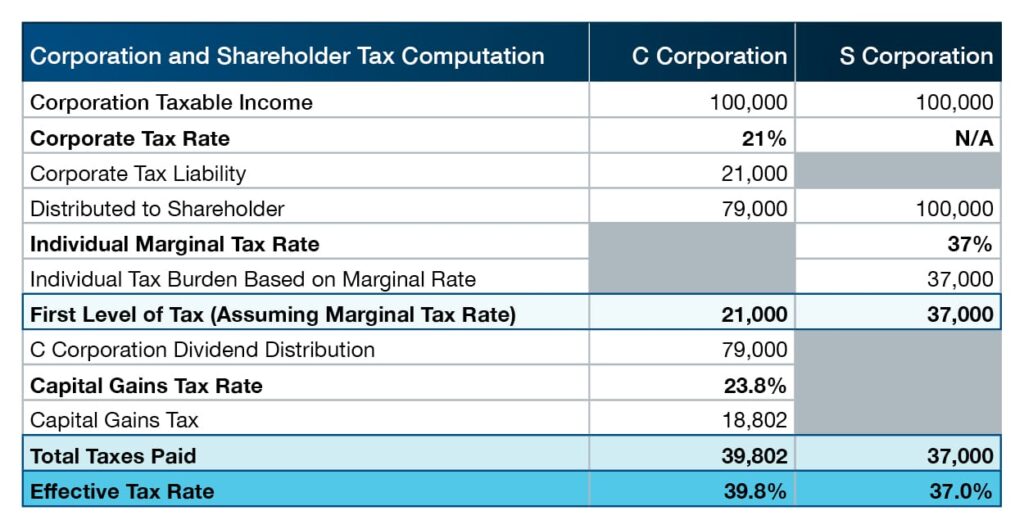
S Corporation Or C Corporation Under The Tax Cuts And Jobs Act Pya
